Hormones are so much more interesting than what we’re taught in health class. So we’ve created a guide to aaaall of the hormones. Here’s everything you need to know about estrogen, progesterone, androgens, progestins, synthetic estrogen, and sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG).
Top things to know:
-
Hormones tell your body how to breathe, grow, drink, and eat
-
If you have a menstrual cycle, your reproductive hormones are constantly shifting throughout your cycle—unless you take certain types of hormonal birth control
-
Hormonal imbalance can be caused by conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, and PCOS
What are hormones?
Hormones are molecules produced by the endocrine system that send messages to various parts of the body. They help regulate your body’s processes, like hunger, blood pressure, and sexual desire. While hormones are essential to reproduction, they are fundamental to all the systems of your body.
Hormones are released from glands in your endocrine system. They tell your body how to breathe and how to expend energy.
Hormones flow through the whole body, but only affect certain cells designed to receive their messages. Hormones and hormone receptor sites work together like a lock and a key (1).
What do hormones do in my body?
All bodies experience hormonal shifts constantly throughout the day.
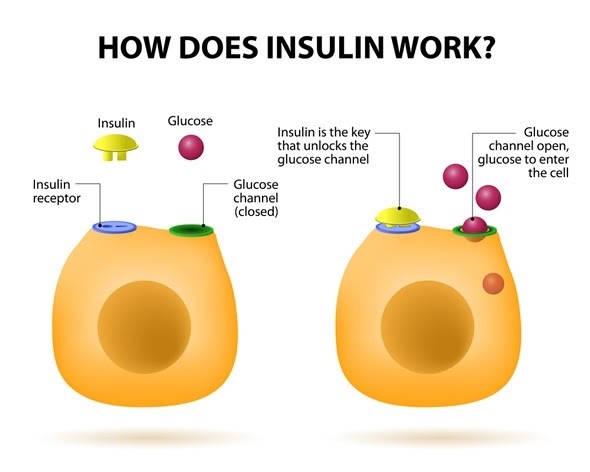
When you eat a meal, the pancreas produces the hormone insulin to help regulate blood sugar. As you slam on the brakes to avoid a car collision, your adrenal glands pump out the hormone adrenaline (epinephrine) to help you act quickly. Your pineal gland works to produce the hormone melatonin to help you get restful sleep at night (1).
When hormones aren’t balanced correctly, an endocrine disorder can be to blame. Having too much of a hormone (also known as hyper-function) or not having enough of a hormone (known as hypo-function), can cause problems.
Hormonal imbalance
Hormonal imbalance can be caused by health conditions. Some of them include:
Tiny but mighty, our bodies depend on hormones to function. Some people are more sensitive to hormones than others. This might explain why some people suffer from premenstrual syndrome (4) or postpartum depression (5), while others aren’t bothered at all by the hormonal changes of menstruation and pregnancy.
Which hormones are responsible for what?
Each hormone-producing gland in the body makes a hormone with a very specialized purpose (6).
-
Hypothalamus: regulates body temperature, hunger, mood, thirst, sleep and libido
-
Pituitary: is the “Wizard of Oz” gland, controlling other glands behind the scenes.
-
Parathyroid: regulates calcium.
-
Pancreas: produces insulin to help use food as energy.
-
Thyroid: regulates heartbeat and how calories are used.
-
Adrenal glands: produce stress hormones.
-
Pineal gland: produces melatonin to regulate the body clock.
-
Ovaries: secrete sex hormones for use in the reproductive cycle.
-
Testes: produces testosterone and sperm (7).
How do hormones affect sex and reproduction?
Reproductive hormones are made by the ovaries and the testicles. The ovaries produce estrogen, progesterone, and androgens, while the testicles produce androgens like testosterone (9).
Puberty, development of breasts, ability to become pregnant or produce sperm, and body hair growth are all influenced by reproductive hormones. The levels of these hormones fluctuate throughout a person’s life, generally declining as a person ages (10).
For women and people with cycles, these hormones shift throughout the menstrual cycle during the reproductive years, unless you introduce hormones into the body with hormonal birth control.
Pregnancy is the time of the most dramatic hormone shift. The body even creates a new organ called the placenta that secretes progesterone (8).
What you need to know about reproductive hormones
The menstrual cycle is more than just your period – it’s a complex ebb and flow of hormones that make your reproductive system function. Without hormones, your reproductive organs would be stagnant. You wouldn’t be able to become pregnant and might not experience the desire to have sex.
While the sex hormones estrogen and testosterone are powerful, they need help from a protein called sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) to function properly. SHBG is like a chaperone that grabs a specific sex hormone, removing it from direct circulation in the body and transporting it to the necessary tissue (11). (You can read more about SHBG and its effect on your body, in depth, in this article.)
The reproductive hormones include:
Androgens
Androgens are made from cholesterol and produced in the adrenal gland and the ovaries (9, 11). Women and people with cycles who have higher levels of androgens than normal can experience symptoms like excess hair growth, acne, irregular or absent periods and infertility (12,13).
Conditions that cause androgen excess include:
(You can read more about androgens and their effect on your body, in depth, in this article.)
Progesterone
Progesterone is the major hormone that promotes pregnancy. It’s easy to remember if you think the word progesterone as “pro-gestation”(15).
During the menstrual cycle, progesterone is low until ovulation. Then, levels rise. Progesterone changes the structure of the endometrium so that a fertilized egg can implant (16).
During pregnancy, progesterone is the primary hormone of the first trimester (15). It also helps to develop breast tissue called mammary glands that are essential for lactation (17).
(You can read more about progesterone and its effect on your body, in depth, in this article.)
Estrogen
Estrogen is associated with menstruation, but it also impacts a number of bodily functions, including bone development and brain, cardiac, vascular and urinary tract health (18).
Perhaps more than any other hormone, estrogen impacts the way we look. It impacts body fat composition and even the health of skin and hair (19).
(You can read more about estrogen and its effect on your body, in depth, in this article.)